Monthly Archives: December 2012
-
Continue Reading »
General
So how does a barcode work?
Essentially, a barcode encodes information in a visual pattern that is readable by a machine. The black and white bars (elements) combination, represents different text characters, which in turn follows a fixed algorithm for that barcode type. If you change the sequence of the elements you will get different text. The barcode scanner device reads this pattern of black and white and turns it into a line of text your computer can process and understand.
Is the price included in the barcode?
A barcode can hold any type of text information you want to encode, but with standard product labels the price is generally not encoded. The main purpose of the barcode is to denote what product it is and your Point of Sale Software or database will have the pricing associated to this product ID.
What is the difference between a 1D (linear) barcode and a 2D barcode?
A 1D (linear) code is the typical black and white stripe style barcode that people are most familiar with. There are several versions of 1D codes, some of them encode only numbers while others can encode keyboard characters, and all the information in the code is organized horizontally, from left to right. These codes can be read by any type of barcode scanner, including 2D scanners. 2D barcodes are more complex because they have to organize information vertically and horizontally. This allows 2D codes to hold more information and take up less space, compared to a 1D code. 2D codes can only be read properly by a an imager scanner.

How many characters fit into a barcode?
It depends on the specific barcode type. 1D barcodes can have for example 20-25 characters whilst 2D barcodes go up to a maximum of 2,000 characters. The only practical concern is that when you increase the amount of information in the barcode, it will become bigger in size, especially with 1D barcodes, and therefore most people encode 8-15 characters.
What is the smallest I can make a barcode?
Barcodes can come in a wide range of sizes and can get down to as small as a 80.645mm² square when using a 2D code. But there is a trade off, since making such a small code will limit the amount of characters you use, and will also require a quality high resolution label printer to print the best quality barcode label possible. The smaller a code becomes, the more difficult it becomes to read by the scanner.
UPC Barcode and UPC Number
Who needs a UPC number?
If you supply products to a distributor or a retailer, you will most likely need a UPC barcode. Contact the company selling your product to find out their policy on UPC barcodes if you are not sure. When you obtain an UPC number, you will also receive a certificate authenticating your number. Most retailers require proof of the certificate to verify that your number is unique and authorized.
Use
Need a UPC?
Selling products through a distributor or retailer
Most of the time
Selling products through a major national store
Always
Tracking internal inventory
No
Selling products directly to customers
No
How do I get a UPC number in Australia?
GS1 AU can issue you a globally unique "GS1 Company Prefix" that is used to create UPC numbers. Click here to apply: Apply for an Australian UPC Barcode
How much does a UPC number cost?
The number of unique products you need to identify and as well as gross sales revenue determines the fee. Prices vary greatly, GS1 can give you an accurate cost for this.
What is a UPC barcode?
You are probably familiar with the barcodes you see on most packaged products. These barcodes are in the UPC-A code format. It is 12 digits long and looks like this:
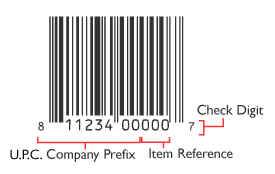
The UPC number itself is known as the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) and is made up of two parts:
- The UPC Company Prefix (see above diagram) and
- The number you have assigned to a unique product.
The UPC Company Prefix is between 6 and 10 digits long, and is assigned to you by GS1 Australia. The number of products you will need to assign numbers to will determine the number of digits required. E.g., if you have thousands of products, your company prefix will need to be fewer digits. If you have just a few products, your company prefix will likely be almost 10 digits long. This company prefix number will represent you as the manufacturer of all of your products, as well as in all the EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) applications.
Your Unique Number, used to reference a specific product, is called an "Item Reference Number." This number is not assigned by GS1 Australia - it is up to the manufacturer to assign the unique Item Reference Number for a product.
The last number on the barcode is a check digit calculated from the previous 11 digits, it is not randomly assigned and the barcode label printing software you use to create your labels will calculate the check digit for you. You can contact POS'99 for help with selecting a label printing software to meet your business needs.
Printing your own UPC barcodes
Once you have a unique GS1 number, contact POS 99 for assistance with selecting a barcode label printer, barcode software, and barcode labels. We can also recommend a compatible and suitable barcode scanner.
More information on UPC from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Product_Code
Printing Barcodes
What is the difference between thermal transfer (TT) and direct thermal (DT)?
The Direct Thermal method uses a label coated with a heat sensitive layer and not a ribbon or ink to print. The image is burned into the paper, with the Thermal Transfer method you use a ribbon to print onto the label. Direct Thermal labels will fade over time (aprox. 12 months) and is not a good choice for environments with high temperatures or sunlight exposure, and Thermal Transfer print is a more permanent and will not fade.
What is 'DPI'?
Dots Per Inch (DPI) is a measure of a printer's resolution, the higher the DPI number the finer the print will be. For most applications, 203 dpi is suitable, but in cases where logos/images or very small labels are being made you want 300 or 600 DPI.
How many labels are on a roll?
It depends on how tall the label is, the shorter the label the more you will get per roll.
How do I make a barcode label?
With your barcode label printer , media and barcode label design software you can create and print a label. The software allows you to place barcodes, text, and images to fit your design requirements and then prints from you label printer.
What’s a dispenser?
A dispenser is an accessory available on most label printers and peels the backing off from the label as it ejects from the printer. This is very useful when you have to apply the label immediately after print, as it saves time for the user. The function can also be disabled if not required.
The difference between 'desktop' and 'tabletop' printers?
Label printers are divided into two categories based on their size and maximum print duty cycle: 1) Desktop printers are smaller than tabletop printers and best for low volume applications such as office labeling or a small retail store. 2) Tabletop printers are meant for high volume scenarios, making hundreds or thousands of labels daily, and are a lot more robust for handling harsher environments.
Barcode Scanning & Scanners
How does a barcode scanner work?
A barcode scanner picks up the alternating black and white elements on the barcode which follows a specific algorithm that is turned into a corresponding text string by the barcode scanner. This information is sent over to your computer by the barcode scanner in the same way a keyboard does. The string of text you scanned will populate where ever your cursor is on screen of the software application you are using at that time. (E.g. Notepad)
Do I need any specific software to use a scanner?
Barcode scanners do not require any specific software or driver to function properly. Your computer will recognised it as a general input device because the scanner emulates itself as a keyboard.
How long is the range of a cordless barcode scanner?
The range of cordless barcode scanners vary by model but most units use Class 2 Bluetooth technology and thus have a range of 10 meters. Some of the rugged barcode scanners use Class 1 Bluetooth which has a range of just over 90 meters.
Can I read a barcode off of a computer screen?
To read a barcode from a computer screen you will need a 2D imaging scanner as it processes images, and not reflected light. A basic laser barcode scanner will not read anything from a computer screen.
How long is the cable on most scanners?
Most barcode scanners come with a 1.8m cable but longer lengths are available for most models.
Can my scanner read a 2D barcode?
2D barcodes require a specific type of scanner, called a 2D Imager. The common laser barcode scanner reads codes by reflecting light from the black and white lines of a barcode and only reads horizontally across the barcode. An imager scanner takes a picture of the barcode and analyses this picture to decode the information. 2D barcodes data are organized vertically and horizontally, therefore only an imager scanner can properly decode all the information.
Mobile Computers
Do mobile computers come with software?
Mobile computers have an operating system installed on it, but not any additional software. There is a wide range of applications you can install on a mobile computer for specific functions such as Mobile POS, asset tracking and warehouse management.
What is 802.11a/b/g/n ?
802.11a/b/g/n is a wireless communication protocol that’s commonly called Wi-Fi and units with this capability access a wireless network in the same way as a PC or laptop.
What is the difference between Windows Mobile/Windows CE and Windows 7/Vista?
The mobile operating systems have a smilar layout as Windows 7/Vista, but are distinct, and are not compatible with each other, in the same way as a version of Excel, that will run on a Windows Mobile device, is not the same as Excel on your desktop PC.
Can I get online with a mobile computer?
Yes, mobile computers offer two ways to get online. Either with Wi-Fi (802.11a/b/g/n) or through a cellular provider's WAN, as long as you are within the coverage of the network and have the right permission/service to join, you can gain access to the Internet.
ID Card Printing explained
Factors to consider when buying an ID Card Printer:
- Security: Consider lamination for security and durability.
- Printing Capability: One or two side printing.
- Volume: Number of cards you plan on printing.
- Printing Technology: Do you need a border printed on the card, or can you have an unprinted border around the card.
- Encoding: Technology you plan on using with the ID card Magnetic stripe or SmartCard.
Do card volumes impact my choice of printer?
Indeed. The cost and capability of a label printer will change based on the number of cards you plan to print. Label printers are grouped into three categories:
- Premium – These are the most robust printers in the industry and they tend to occupy a larger footprint and offer more options for lamination and other printing technologies. The printers in this category typically handle a volume of 10,000 – 30,000 prints and it is designed for high volume and high security requirements.
- Standard – These printers are a step up in design and printing capabilities. This class of printer also offers reliable print output with a moderate footprint. The printers in this category typically can handle 1,000 – 10,000 prints and works well for small and medium businesses.
- Value – These are the most economical of all the ID Card printers, with a limited footprint and scaled down printing capabilities, this printer is perfect for small printing jobs and perfect for print volumes under 1,000 prints.
Should I buy a single or dual side printer?
Single Side printers are ideal for ID cards with limited cardholder information and Dual Side printers are ideal for situations when significant amounts of data need to be captured on the card. Some information can be moved to the back of the card, so that the front remains uncluttered with fewer distractions.
What’s the difference between “Direct to card” and “Reverse transfer”?
Reverse Transfer is less common and transfers an image to a retransfer film. The film is applied to the blank card which provides "over the edge" coverage and a vibrant, durable print.
Direct to Card (DTC) is the most common card printing technology and basically heats a print ribbon beneath a thermal print head. The color is transferred to a blank card, and the images have sharp edges, deep blacks and also a full spectrum of colors. There is an unprinted border around the card, printing close to the edge can cause expensive print head damage in DTC printers.
Do I have to laminate my ID Cards?
Lamination on an ID Card printer provide the following benefits:
- Cost savings: Printers with laminating capabilities have a larger upfront cost, but they yield significant cost savings further down the road due to the elimination of security incidents and also due to a reduction of card printing supplies.
- Durability: Lamination provides extra durability for standard ID Cards and purchasing a printer with a laminating option is ideal for cards used in harsh conditions/environments and situations where continual use provides excessive wear and tear on the cards.
- Security: Lamination provides an extra layer of security for the ID card by reducing the possibility of counterfeiting and also reducing the risk of tampering with the information contained in the card.
What encoding options do I have for my card?
- Contact Smart Card: A small contact area on the card, comprised of several gold-plated contact pads are embedded onto the card. These pads provide electrical connectivity when touched to or inserted into a reader
- Magnetic Stripe: These cards are capable of storing data on a band of magnetic material/strip. The magnetic stripe (also commonly known as swipe card or magstripe) is read with physical contact when swiped past a magnetic reading head.
- Gen 2 UHF RFID: RFID cards store data that’s read through radio waves at wider read ranges, and allow multiple card reads at the same time, and are extremely secure
- Contactless Smart Card: These cards contain a re-writeable smart card microchip that can process and store data, they also communicate with a terminal via radio

